- Overview
- Apple Mail
- Apple Numbers
- Apple Scripting
- Excel
- Release Notes
- About the Excel activity package
- Project compatibility
- Supported character encoding
- Project settings
- Add or Update Excel Sensitivity Label
- Append Range
- Auto Fill
- Autofit Range
- Change Pivot Data Source
- Clear Sheet/Range/Table
- Copy/Paste Range
- Create Pivot Table
- Delete Column
- Delete Rows
- Delete Sheet
- Duplicate Sheet
- Export to CSV
- Fill Range
- Filter
- Filter Pivot Table
- Find First/Last Data Row
- Find/Replace Value
- For Each Excel Row
- For Each Excel Sheet
- Format As Table
- Format Cells
- Get Cell Color
- Get Excel Chart
- Get Excel Sensitivity Label
- Get Selected Range
- Insert Column
- Insert Chart
- Insert Rows
- Insert Sheet
- Invoke VBA
- Lookup
- Match Function
- Protect Sheet
- Read Cell Formula
- Read Cell Value
- Read Range
- Refresh Excel Data Connections
- Refresh Pivot Table
- Remove Duplicates
- Rename Sheet
- Run Spreadsheet Macro
- Save Excel File
- Save Excel File As
- Save Excel File As PDF
- Select Range
- Sort Range
- Text to Columns
- Unprotect Sheet
- Update Excel Chart
- Use Excel File
- VLookup
- Write Cell
- Write CSV
- Write DataTable to Excel
- Excel Application Scope
- Append To CSV
- Read CSV
- Write CSV
- Delete Column
- Filter Table
- Get Table Range
- Insert Column
- Sort Table
- Append Range
- Close Workbook
- Get Cell Color
- Read Cell
- Read Cell Formula
- Read Column
- Read Range
- Read Row
- Select Range
- Set Range Color
- Write Cell
- Write Range
- Save Workbook
- Create Table
- Get Workbook Sheet
- Get Workbook Sheets
- Refresh Pivot Table
- Create Pivot Table
- Get Selected Range
- Copy Sheet
- Delete Range
- Auto Fill Range
- Copy Paste Range
- Execute Macro
- Insert/Delete Columns
- Insert/Delete Rows
- Invoke VBA
- LookUp Range
- Remove Duplicates Range
- Excel Process Scope
- Manage CSV Files
- Filter CSV Files
- Verify CSV Files
- Compare CSV Files
- Sort Data in Excel Files
- Filter and Delete Rows in Excel Files
- Read, Write, and Append Data in Excel
- Table Functions
- Read From Excel Files
- Manage Multiple Excel Files
- Filter Excel files by cell color
- Verify Excel Workbook Data
- Compare Numeric Values
- Interpret Excel Results
- Manage Range Selection
- Manipulate Range Selections
- Manage Pivot Tables
- Manage Databases in Excel
- Google Workspace
- Release notes
- About the Google Workspace activities package
- Project compatibility
- Project settings
- Google Workspace HTTP Request
- Run Script
- Apply File Labels
- Clear File Label Fields
- Copy File
- Create Folder
- Delete File or Folder
- Delete File or Folder Permission
- Download File
- For Each File or Folder
- Get Drive Labels
- Get File or Folder Info
- Get File Labels
- Get File/Folder
- Get File List
- Get File or Folder Permissions
- Move File
- Remove File Labels
- Rename File or Folder
- Share File or Folder
- Update File or Folder Permission
- Upload Files
- Apply Gmail Labels
- Archive Email
- Delete Email
- Download Email
- Download Email Attachments
- For Each Email
- Forward Email
- Get Email by ID
- Get Email List
- Get Gmail Labels List
- Get Email Thread
- Get Newest Email
- Get Single Gmail Label
- Mark Email as Read/Unread
- Move Email
- Remove Gmail Labels
- Reply to Email
- Send Email
- Turn On Automatic Replies
- Turn Off Automatic Replies
- Wait for Calendar Event Created and Resume
- Wait for Calendar Event Received and Resume
- Wait for Calendar Event Replied and Resume
- Wait for Calendar Event Updated and Resume
- Wait for Email Received and Resume
- Wait for Email Sent and Resume
- Wait for File Created and Resume
- Wait for File Updated and Resume
- Wait for Folder Created and Resume
- Wait for Sheet Created and Resume
- Wait for Sheet Cell Updated and Resume
- Wait for Row Added to the Bottom of a Sheet
- Wait for Task Created and Resume
- Wait for Task Completed and Resume
- Add Attendee
- Create Event
- Delete Event
- Modify Event
- Search Events
- Use Google Drive
- Share File
- Delete File Permission
- Get File Permissions
- Update File Permission
- Copy File
- Create Folder
- Delete File
- Download File
- Find Files and Folders
- Get File Info
- Move File
- Upload File
- Create Document
- Create New Spreadsheet
- Get Mail Messages
- Send Mail Messages
- Change Labels
- Use Google Spreadsheet
- Add Delete Columns
- Add Delete Rows
- Auto Fill Range
- Add New Sheet
- Append Row
- Batch Spreadsheet Updates
- Copy Sheet
- Copy Paste Range
- Delete Range
- Delete Sheet
- Get Cell Color
- Get Sheets
- Read Cell
- Read Column
- Read Range
- Read Row
- Rename Sheet
- Write Cell
- Write Range
- Clear Range
- Download Spreadsheet
- Use Google Document
- Batch Document Updates
- Get Document
- Get Text Index
- Insert Text
- Replace Text
- Read All Text
- Create Script Project
- Get Project Content
- Upload Script File
- Create Deployment
- Run Script
- Mail
- Microsoft 365
- Release notes
- About the Microsoft 365 activity package
- Project compatibility
- Project settings
- Microsoft 365 HTTP Request
- List All Records
- Assign Sensitivity Label
- Create Folder
- Copy File/Folder
- Delete File or Folder
- Download File
- File Check-in/Check-out
- For Each File or Folder
- Get File/Folder
- Get File or Folder Metadata
- Get Sensitivity Labels
- Get File or Folder List
- Move File/Folder
- Rename file or folder
- Share File/Folder
- Upload Files
- Update File or Folder Metadata
- Archive Email
- Delete Email
- Download Email
- Download Email Attachments
- For Each Email
- Forward Email
- Get Email By ID
- Get Email Folders List
- Get Email List
- Get Email Thread
- Get Newest Email
- Mark Email as Read or Unread
- Move Email
- Reply to Email
- Send Email
- Set Email Categories
- Turn On Automatic Replies
- Turn Off Automatic Replies
- Wait for Calendar Event Created and Resume
- Wait for Calendar Event Received and Resume
- Wait for Calendar Event Replied and Resume
- Wait for Calendar Event Updated and Resume
- Wait for Cell in Worksheet Updated and Resume
- Wait for Email Received and Resume
- Wait for Email Sent and Resume
- Wait for File Created and Resume
- Wait for File Updated and Resume
- Wait for Row Added to the Bottom of a Table and Resume
- Wait for List Item Added and Resume
- Wait for List Item Updated and Resume
- Wait for Worksheet Created and Resume
- Connections
- AddEmailCategories
- ArchiveEmail
- DeleteEmail
- DownloadEmail
- DownloadEmailAttachment
- DownloadEmailAttachments
- ForwardEmail
- GetEmail
- GetEmailAttachmentsInfo
- GetEmails
- GetMailFolders
- GetNewestEmail
- MarkEmailAsRead
- MarkEmailAsUnread
- MoveEmail
- RemoveEmailCategories
- ReplyToEmail
- SendEmail
- TurnOffAutomaticReplies
- TurnOnAutomaticReplies
- Merge multiple sheets into a new summary Excel sheet
- Automatically accept calendar invites from your manager
- Move files to dedicated folders by type
- Verify if new employment documents (I9 and ID) match
- Add new customers to a SharePoint List
- Delete SharePoint List items newer than yesterday
- Notify me on Slack when an important Outlook Email is received
- Include creation date in new OneDrive file names
- Notify me by email when a new file is created
- Microsoft 365 Scope
- Add Sheet
- Append Range
- Clear Range
- Copy Range
- Copy Sheet
- Create Workbook
- Delete Range
- Delete Sheet
- Get Cell Color
- Get Sheets
- Read Cell
- Read Column
- Read Range
- Read Row
- Rename Sheet
- Write Cell
- Write Range
- Set Range Color
- Create Table
- Get Table Range
- Insert Column
- Delete Column
- Insert Rows
- Delete Rows
- VLookup Range
- Use OneDrive & SharePoint
- Copy File/Folder
- Create Folder
- Delete File/Folder
- Download File
- Export File as PDF
- Find Files And Folders
- Get File/Folder
- Move File/Folder
- Upload File
- Share File/Folder
- For Each File/Folder
- Forward Mail
- Find Meeting Times
- Get Mail
- Move Mail
- Send Mail
- Reply to Mail
- Delete Mail
- Set Mail Categories
- Add Attachment
- Add Attendee
- Add Location
- Create Event
- Delete Event
- Get Calendars
- Modify Event
- RSVP
- Search Events
- Create Group
- Delete Group
- Get Group
- List Groups
- Create Bucket
- Delete Bucket
- List Buckets
- List Bucket Tasks
- Create Plan
- Get Plan
- List Plans
- Create Task
- Delete Task
- Get Task
- List Tasks
- Update Task
- For Each List
- Get List Info
- For Each List Item
- Delete List Item
- Add List Items
- Update List Item
- Get List Items
- Authentication troubleshooting
- AADSTS50011: Redirect URI mismatch
- AADSTS50076: Using multifactor authentication
- AADSTS50079: The user is required to use multifactor authentication
- AADSTS500113: No reply address registered for the application
- AADSTS900971: No reply address provided
- AADSTS65001: The user or administrator has not consented to use the application
- AADSTS65004: User declined to consent to access the app
- AADSTS7000218: The request body must contain the following parameter: client_assertion or client_secret
- AADSTS700025: Client is public so neither 'client_assertion' nor 'client_secret' should be presented
- AADSTS70002: InvalidClient - Error validating the credentials
- AADSTS7000215: Invalid client secret provided
- AADSTS50055: The password is expired
- AADSTS700082: The refresh token has expired due to inactivity
- AADSTS50194: Application is not configured as a multitenant application
- AADSTS53003: Access has been blocked by Conditional Access policies
- Mail troubleshooting
- Calendar troubleshooting
- Files troubleshooting
- Sheets troubleshooting
- Presentations
- Release Notes
- About the Presentations activity package
- Project compatibility
- Add or Update Powerpoint Sensitivity Label
- Add Data Table to Slide
- Add File to Slide
- Add Image or Video to Slide
- Add New Slide
- Add Text to Slide
- Copy Paste Slide
- Create New PowerPoint Document
- Delete Slide
- Format Slide Content
- Get Powerpoint Sensitivity Label
- Paste Item Into Slide
- Replace Text in Presentation
- Run Presentation Macro
- Save PowerPoint File As
- Save Presentation as PDF
- Use PowerPoint Presentation
- Word
- Release Notes
- About the Word activities package
- Project compatibility
- Word Application Scope / Use Word File
- Add or Update Word Sensitivity Label
- Add Hyperlink to Document
- Add Picture
- Append Text
- Create New Document
- Get Word Sensitivity Label
- Insert DataTable in Document
- Paste Chart/Picture Into Document
- Read Text
- Replace Picture
- Replace Text in Document
- Save Document As
- Save Document as PDF
- Set Bookmark Content

Productivity activities
Interactive token
Overview
The interactive token authentication type includes the following characteristics:
- Runs as a user.
- Used in attended automation scenarios.
- Uses delegated permissions.
This is the same authentication method that Integration Service supports either through the UiPath Public App or the Bring your own app method.
Details
You can use the Interactive Token authentication type for attended automation, and when multi-factor authentication (MFA) is required. If you want to test the activity package, use this authentication method, as it is easy to configure and works well for personal accounts. The interactive token uses the default redirect URI mentioned in the Registering your application section.
You can either use the UiPath Public App (OAuthApplication = UiPath), which is the default one, or you can register and use your own Azure app (OAuthApplication = Custom):
- UiPath Public App registration: The advantage of using the UiPath public app is that you do not need to configure or maintain the application.
UiPath does not store any user data. The authentication token is saved only on your machine or in your Orchestrator bucket. For more details, check UiPath Public App registration.
- Bring your own app (BYOA): The advantage of using your own application is that you can manage, customize, and assign permissions within your organization more granularly. For more details, check Custom OAuth Application registration - Bring your own app (BYOA).
For more details on how to set up the OAuth application, check OAuth application setup.
When you create an application, you must select an application type. For interactive token authentication, use a mobile or desktop application that uses the OAuth 2.0 authorization code flow with a Redirect URI of type public client or native (mobile and desktop).
When you run the Microsoft 365 activity for the first time with the interactive token authentication type, you are prompted to authorize access to the resources you granted permissions to when registering your app. For more details, check Get access on behalf of a user.
A single organization can have multiple application (client) IDs. Each application ID contains its own permissions and authentication requirements. For example, you and your colleague can both register a Microsoft 365 application in the Microsoft Entra ID of your company with different permissions. Your app can be configured to authorize permissions to interact with files only, while the app of your colleague can authorize permissions to interact with files, mail, and calendar.
- If you select the interactive token authentication type in the Microsoft 365 Scope activity, leave the Username and Password fields empty.
- If you are using a single-tenant app, configure the Tenant field.
- If you are using a multi-tenant app, such as the UiPath public app, leave the Tenant field empty.
Scopes for Interactive token
This section applies to both UiPath Public App and Bring your own app methods.
When you add an activity to Microsoft 365 Scope, Studio automatically detects the scopes it requires. You can also allow additional or fewer scopes. However, if fewer scopes are selected, some activity functionalities might not work.
For more details, check Working with activity scopes.
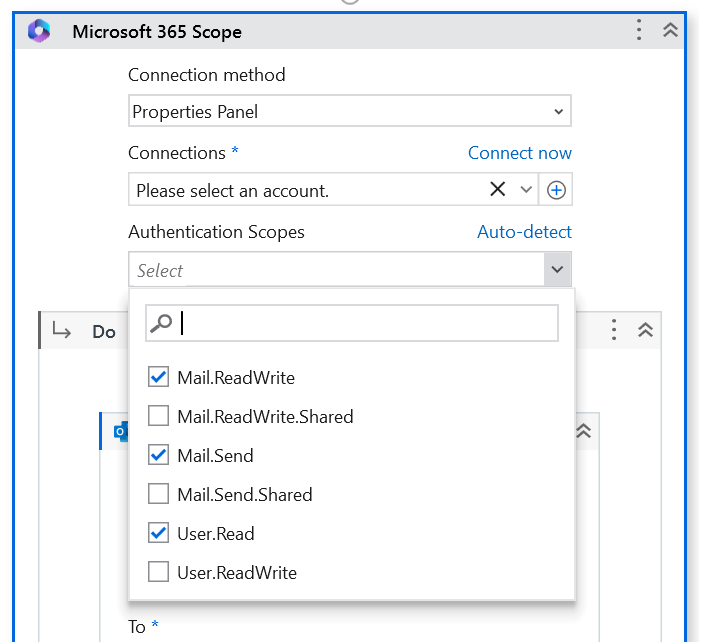
For more details, check the following resources:
Building your project in Studio Desktop
First, create a new automation project as follows:
- In UiPath Studio, select New Project.
- Select Process, which opens a New Blank Process window.
- Enter a project Name, Location, and Description.
- Select the Compatibility, where Windows is selected by default.
- Select Create.
- For more information about UiPath Studio packages, check Managing Packages.
After you create your project, install the UiPath.MicrosoftOffice365.Activities package as follows:
- Select Manage Packages from the Design ribbon.
- Enter Office 365 or Microsoft in the search bar, under All Packages.
- Select the package version you want, then select Install.
- Select Save.
You're done! Now that you have completed the setup, you can start adding the Microsoft 365 activities to your project.
Next steps
For a hands-on learning experience and to quickly start using the activities, check the Quickstart guides. These guides provide step-by-step instructions to help you create working samples of the different activities so that you can verify the connection to your registered app and get familiar with the input/output properties.
To learn more about the Microsoft 365 activities (including example property inputs/outputs), check the Classic activities for a complete list and links to the activity detailed pages.