- Getting started
- For administrators
- RPA workflow projects
- Creating an RPA workflow from an idea
- Creating a project
- How to start an RPA workflow
- Managing project files and folders
- Connecting RPA workflows to your accounts
- Configuring activities
- Managing the activities in a project
- Passing values between activities
- Iterating through items
- Managing the data in a project
- Configuring a project to use your data
- Using file and folder resources
- App projects
- Agentic processes
- Agents
- Solutions
- API workflows
- Tests

Studio Web user guide
Validation Control
Validation Control is a component within Apps in Studio Web that embeds Validation Station from Document Understanding into your apps. This allows you to review, correct, or approve data that has been automatically extracted from documents, such as invoices, forms, or emails. Common scenarios include human-in-the-loop automations, especially when data extraction is uncertain or incomplete. For example, if an invoice is scanned and the total amount looks uncertain, the Validation Control allows a human to check and correct it before submission.
Validation Control lets you manually review documents directly in your web app, especially when:
- data is missing or unclear
- confidence levels are low
- human judgment is required to validate business rules
User scenarios
Examples of Validation Control user scenarios include:
- Approving invoices that have uncertain totals
- Reviewing insurance claims with partially extracted data
- Confirming names and addresses when the document is low quality
Capabilities
Integrating Validation Control in your app lets you:
- View the full document directly within the app interface.
- See extracted data, such as names, amounts, dates.
- Edit, confirm, or delete data.
- Trigger business rules or workflows based on user input.
- Validate multiple document types, table values, and complex field structures.
- Secure data exchange through Automation Cloud, using storage buckets to store and retrieve all document validation content.
How it works
The main workflow is as follows:
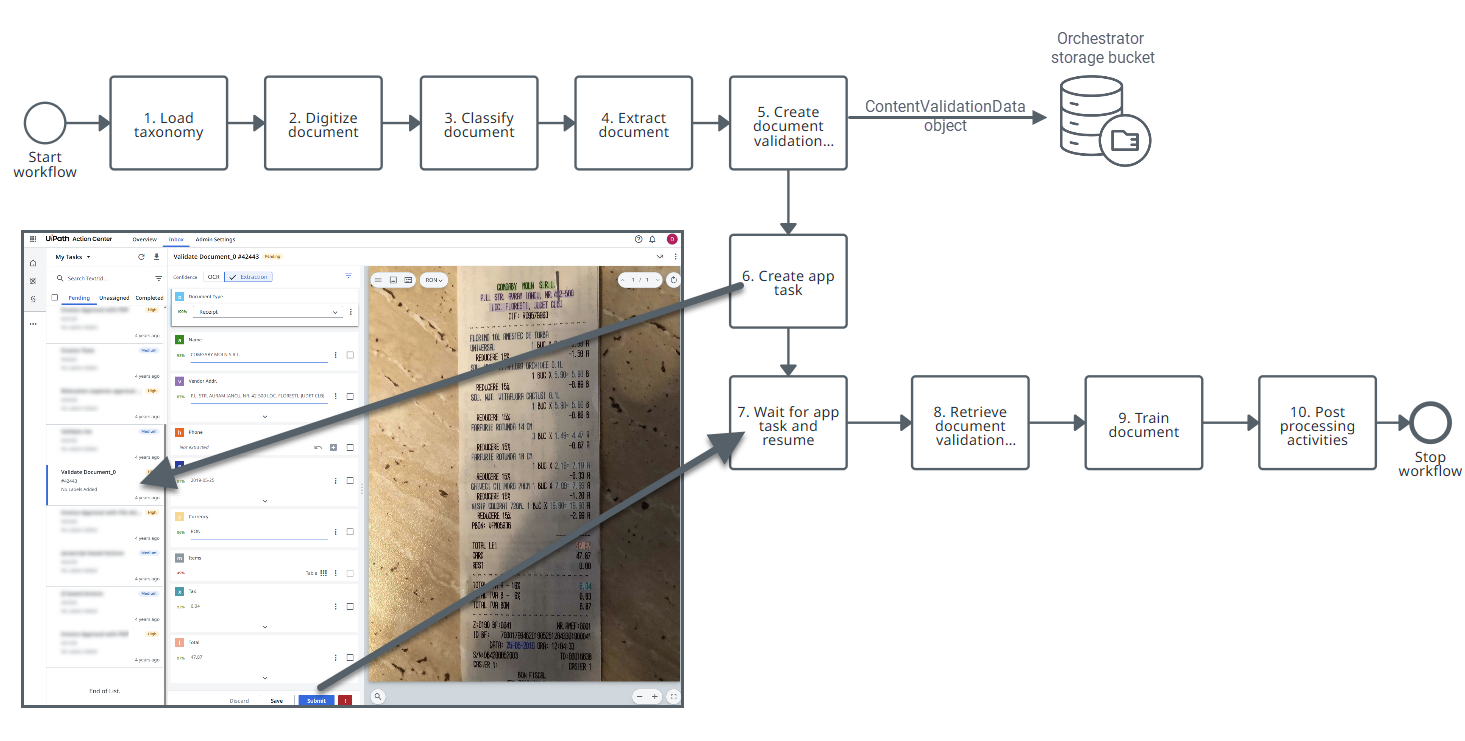
1, 2, 3, 4: You upload a document for extraction. The robot procceses your document using Document Understanding or Communications Mining.
5: The robot uses Create Document Validation Artifacts or Create Communication Mining Validation Artifacts activities to create an output object of the ContentValidationData class . This object includes the extracted results, the original document, and supporting information.
The activity then creates and stores all the intermediate data that the Validation Control needs to display the document and its extraction details. This data is saved in an Orchestrator storage bucket, and you can access it using the ContentValidationData object.
6: The robot that extracted your data triggers an action app that includes Validation Control. This application is presented to you as an Action Center task.
If you are building a standalone app, instead of adding steps 6 (Create app task) and 7 (Wait for app task and resume), you can assign the ContentValidationData object to the ContentValidationData variable. You can use this variable as the data source of the Validation Control.
7: You, as the user, receive a task in the Action Center. You open the web app and see the document on one side and the extracted data on the other. You can then correct values, confirm data, or reject incorrect entries.
8, 9, 10: Once you submit the validated data, the robot uses the Retrieve Document Validation Artifacts or Retrieve Communications Mining Validation Artifacts activities to retrieve the updated information, and then resumes the automation. This ensures the workflow uses only reviewed and approved data.
Limitations
When using Validation Control in your app, keep the following limitations in mind:
- You can only use it in Automation Cloud. On-premise or hybrid environments are not supported.
- Validation Control works only in Studio Web App Projects. You cannot use it in VB Apps.
- You can use it only for Document Validation tasks. It does not support Document Classification at this time.
The ContentValidationData object
The ContentValidationData object is the data required for the Validation Control to load and render a document and its extraction details. It serves as the data source for the control.
This object is created and stored in an Orchestrator storage bucket by the Create Document Validation Artifacts or Create Communications Mining Validation Artifacts activities. When a task is completed, you can use the ContentValidationData object as an input for the Retrieve Document Validation Artifacts or Retrieve Communications Mining Validation Artifacts activities to retrieve the validated information.
The ContentValidationData JSON structure
You can access the ContentValidationData object in a JSON format from the workflow logs, after you enable log activities. This JSON tells the Validation Control exactly where to find all the files it needs in the storage bucket, to display the document and its extracted data. An example of a serialized ContentValidationData object in JSON format is as follows:
{
"BucketName":"DUValidationStationTestSb",
"BucketId":186140,
"FolderId":756377,
"FolderKey":"c2751834-1f05-4f4e-9cb8-509406f6faac",
"DocumentId":"4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a",
"DocumentPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-
4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a\\CMS 1500.zip",
"EncodedDocumentPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-
e80a2640de8a\\encoded.zip",
"TextPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-
e80a2640de8a\\text.zip",
"DocumentObjectModelPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-
e80a2640de8a\\dom.zip",
"TaxonomyPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-
e80a2640de8a\\taxonomy.zip",
"AutomaticExtractionResultsPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-
e80a2640de8a\\input_results.zip",
"ValidatedExtractionResultsPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-
e80a2640de8a\\output_results.zip",
"ExtractorPayloadsPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-
e80a2640de8a\\extractor_payloads.zip",
"ShowOnlyRelevantPageRange":false,
"AdditionalDataPath":"",
"OriginalDocumentFileName":"CMS 1500.pdf",
"CustomizationInfoPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-
e80a2640de8a\\customization_info.zip"
}
{
"BucketName":"DUValidationStationTestSb",
"BucketId":186140,
"FolderId":756377,
"FolderKey":"c2751834-1f05-4f4e-9cb8-509406f6faac",
"DocumentId":"4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a",
"DocumentPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-
4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a\\CMS 1500.zip",
"EncodedDocumentPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-
e80a2640de8a\\encoded.zip",
"TextPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-
e80a2640de8a\\text.zip",
"DocumentObjectModelPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-
e80a2640de8a\\dom.zip",
"TaxonomyPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-
e80a2640de8a\\taxonomy.zip",
"AutomaticExtractionResultsPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-
e80a2640de8a\\input_results.zip",
"ValidatedExtractionResultsPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-
e80a2640de8a\\output_results.zip",
"ExtractorPayloadsPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-
e80a2640de8a\\extractor_payloads.zip",
"ShowOnlyRelevantPageRange":false,
"AdditionalDataPath":"",
"OriginalDocumentFileName":"CMS 1500.pdf",
"CustomizationInfoPath":"v1\\4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-
e80a2640de8a\\customization_info.zip"
}
Where:
BucketNameandBucketId—These properties indicate the storage bucket where all the files related to the document validation are stored.FolderIdandFolderKey—These properties indicate specific folder within the storage bucket where the document and its related files are located.DocumentId—A unique identifier for the specific document being validated.DocumentPath—The full path to the original document file within the storage bucket.EncodedDocumentPath,TextPath,DocumentObjectModelPath,TaxonomyPath—These are paths to various intermediate files also stored in the bucket. These files are essential for the Validation Control to render the document correctly. They include data such as the document layout information (DocumentObjectModelPath) and the full text (TextPath).AutomaticExtractionResultsPath—The path to the file containing the data that was automatically extracted by the robot.ValidatedExtractionResultsPath—This is where the final, validated data is saved after the validation is complete.OriginalDocumentFileName—The name of the original file.
Using ContentValidationData as Data source
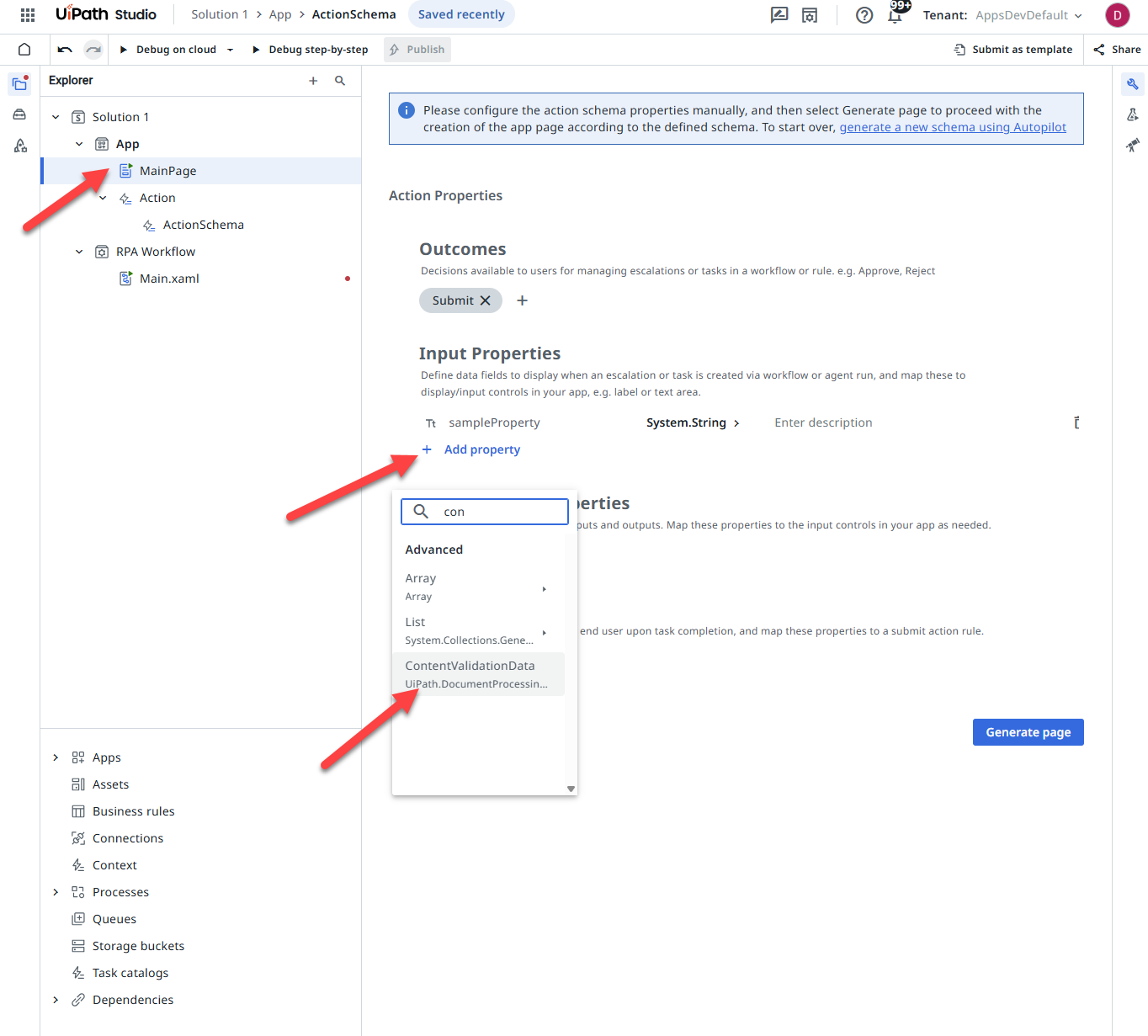
If you use the Create Document Validation Artefacts activity, you can assign the resulting ContentValidationData object directly to the Validation Control as its data source. To do this, you must:
-
Add an Action app to your project.
-
For the Input Properties of the ActionSchema, select + Add property.
-
Search for the
ContentValidationDataobject, select it, and provide a name for it. For example, "cvd". -
Set the Data Source field of the Validation Control to the action input property ("cvd"). This sets AcctionProperties.cvd as the data source of your Validation Control.
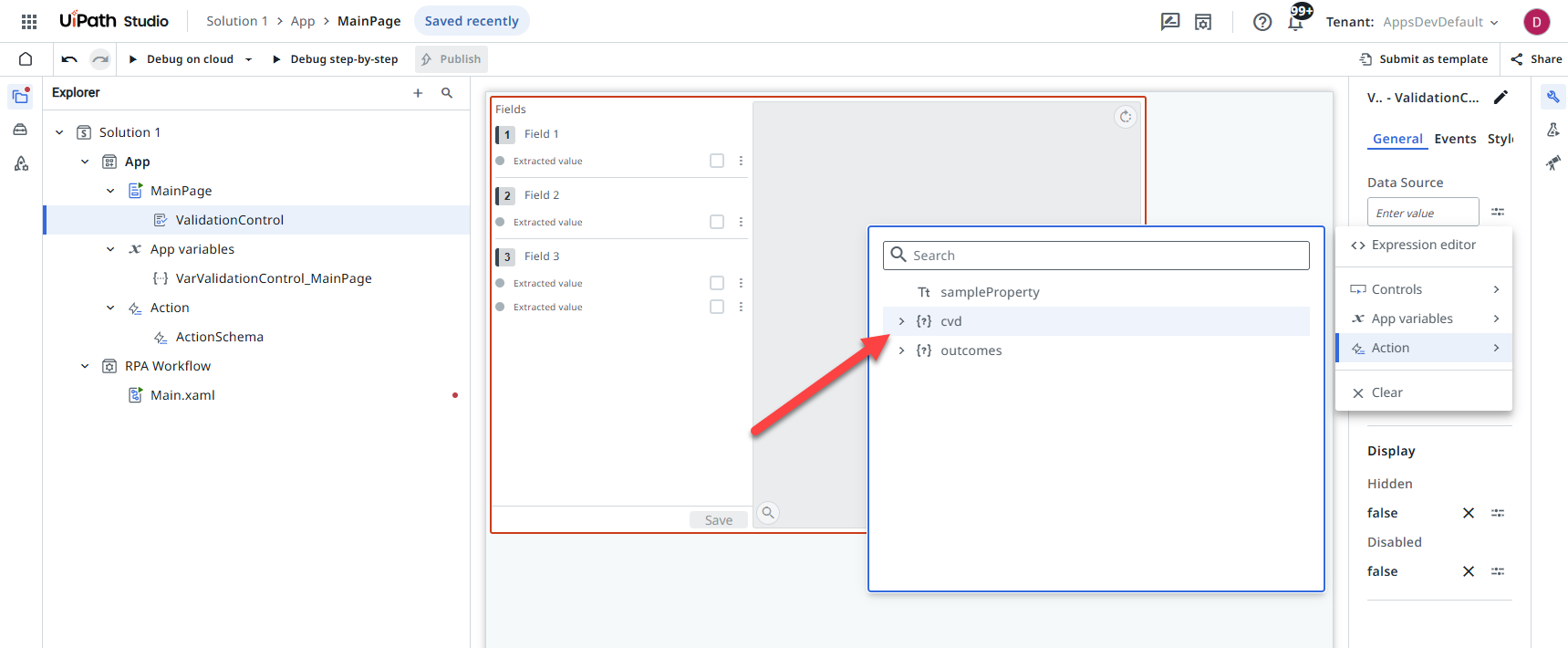
However, when manually creating a JSON object, you cannot use it directly with the Validation Control. You must first convert it into a Visual Basic (VB) expression with a simplified set of properties, such as BucketId, FolderKey, DocumentId.
For example:
New UiPath.DocumentProcessing.Contracts.Actions.ContentValidationData With {
.BucketId = 186140,
.FolderKey =
new Guid("c2751834-1f05-4f4e-9cb8-509406f6faac"),
.DocumentId = "4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a",
.DocumentObjectModelPath = "v1/4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a/dom.zip",
.TaxonomyPath = "v1/4e32cef6-
d4ee-4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a/taxonomy.zip",
.TextPath = "v1/4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a/text.zip",
.EncodedDocumentPath = "v1/4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a/encoded.zip",
.AutomaticExtractionResultsPath
= "v1/4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a/input_results.zip",
.CustomizationInfoPath = "v1/4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a/customization_info.zip"
}
New UiPath.DocumentProcessing.Contracts.Actions.ContentValidationData With {
.BucketId = 186140,
.FolderKey =
new Guid("c2751834-1f05-4f4e-9cb8-509406f6faac"),
.DocumentId = "4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a",
.DocumentObjectModelPath = "v1/4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a/dom.zip",
.TaxonomyPath = "v1/4e32cef6-
d4ee-4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a/taxonomy.zip",
.TextPath = "v1/4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a/text.zip",
.EncodedDocumentPath = "v1/4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a/encoded.zip",
.AutomaticExtractionResultsPath
= "v1/4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a/input_results.zip",
.CustomizationInfoPath = "v1/4e32cef6-d4ee-4eac-a382-e80a2640de8a/customization_info.zip"
}
You can use this approach as an advanced way to troubleshoot your app without creating an Action Center task.