- Getting Started
- Setup and Configuration
- Automation Projects
- Dependencies
- Types of Workflows
- Control Flow
- File Comparison
- Automation Best Practices
- Source Control Integration
- Debugging
- Logging
- The Diagnostic Tool
- Workflow Analyzer
- About Workflow Analyzer
- ST-NMG-001 - Variables Naming Convention
- ST-NMG-002 - Arguments Naming Convention
- ST-NMG-004 - Display Name Duplication
- ST-NMG-005 - Variable Overrides Variable
- ST-NMG-006 - Variable Overrides Argument
- ST-NMG-008 - Variable Length Exceeded
- ST-NMG-009 - Prefix Datatable Variables
- ST-NMG-011 - Prefix Datatable Arguments
- ST-NMG-012 - Argument Default Values
- ST-NMG-016 - Argument Length Exceeded
- ST-NMG-017 - Class name matches default namespace
- ST-DBP-002 - High Arguments Count
- ST-DBP-003 - Empty Catch Block
- ST-DBP-007 - Multiple Flowchart Layers
- ST-DPB-010 - Multiple instances of [Workflow] or [Test Case]
- ST-DBP-020 - Undefined Output Properties
- ST-DBP-021 - Hardcoded Timeout
- ST-DBP-023 - Empty Workflow
- ST-DBP-024 - Persistence Activity Check
- ST-DBP-025 - Variables Serialization Prerequisite
- ST-DBP-027 - Persistence Best Practice
- ST-DBP-028 - Arguments Serialization Prerequisite
- ST-USG-005 - Hardcoded Activity Properties
- ST-USG-009 - Unused Variables
- ST-USG-010 - Unused Dependencies
- ST-USG-014 - Package Restrictions
- ST-USG-017 - Invalid parameter modifier
- ST-USG-020 - Minimum Log Messages
- ST-USG-024 - Unused Saved for Later
- ST-USG-025 - Saved Value Misuse
- ST-USG-026 - Activity Restrictions
- ST-USG-027 - Required Packages
- ST-USG-028 - Restrict Invoke File Templates
- ST-USG-032 - Required Tags
- ST-USG-034 - Automation Hub URL
- Variables
- Arguments
- Imported Namespaces
- Coded automations
- Introduction
- Registering custom services
- Before and After contexts
- Generating code
- Generating coded test case from manual test cases
- Troubleshooting
- Trigger-based Attended Automation
- Object Repository
- The ScreenScrapeJavaSupport Tool
- Extensions
- About extensions
- SetupExtensions tool
- UiPathRemoteRuntime.exe is not running in the remote session
- UiPath Remote Runtime blocks Citrix session from being closed
- UiPath Remote Runtime causes memory leak
- UiPath.UIAutomation.Activities package and UiPath Remote Runtime versions mismatch
- The required UiPath extension is not installed on the remote machine
- Screen resolution settings
- Group Policies
- Cannot communicate with the browser
- Chrome extension is removed automatically
- The extension may have been corrupted
- Check if the extension for Chrome is installed and enabled
- Check if ChromeNativeMessaging.exe is running
- Check if ComSpec variable is defined correctly
- Enable access to file URLs and Incognito mode
- Multiple browser profiles
- Group Policy conflict
- Known issues specific to MV3 extensions
- List of extensions for Chrome
- Chrome Extension on Mac
- Group Policies
- Cannot communicate with the browser
- Edge extension is removed automatically
- The extension may have been corrupted
- Check if the Extension for Microsoft Edge is installed and enabled
- Check if ChromeNativeMessaging.exe is running
- Check if ComSpec variable is defined correctly
- Enable access to file URLs and InPrivate mode
- Multiple browser profiles
- Group Policy conflict
- Known issues specific to MV3 extensions
- List of extensions for Edge
- Extension for Safari
- Extension for VMware Horizon
- Extension for Amazon WorkSpaces
- SAP Solution Manager plugin
- Excel Add-in
- Studio testing
- Troubleshooting
- About troubleshooting
- Assembly compilation errors
- Microsoft App-V support and limitations
- Internet Explorer X64 troubleshooting
- Microsoft Office issues
- Identifying UI elements in PDF with Accessibility options
- Repairing Active Accessibility support
- Validation of large Windows-legacy projects takes longer than expected

Studio user guide
Using Coded automation in Low-Code workflow
In this tutorial, you can learn how to incorporate a coded automation called CodedResetAssetValue.cs into a low-code workflow. The CodedResetAssetValue.cs automation performs the following steps:
- Retrieves the current value of a specific asset from Orchestrator.
- Compares the retrieved asset value with the input value provided as an argument.
- If the previous asset value does not match the input value, it updates the asset value in Orchestrator.
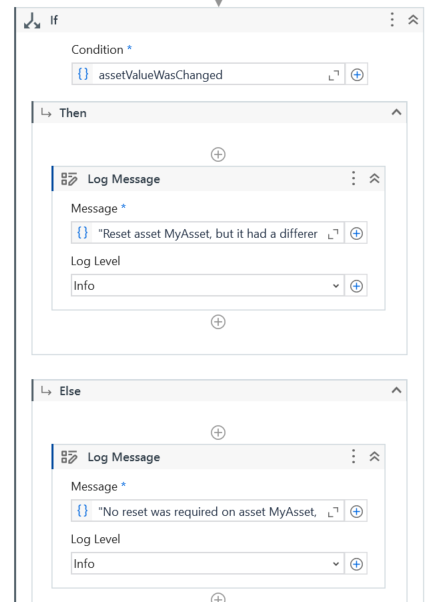
- Logs messages that indicate the status of the asset value, whether it was updated or remained unchanged.
To use a coded automation inside a low-code workflow, first create the coded workflow, then invoke it in the low-code workflow using the Invoke Workflow File activity. Perform the following steps to incorporate a coded automation within a low-code workflow:
-
Create a new coded workflow. For this example, name it
CodedResetAssetValue.- Give the following return arguments to the
Executemethod to indicate if the asset value was changed and to provide the asset value:(bool assetValueWasChanged, string assetValue) - For the
Executemethod, add the following input parameters:assetName (string)andassetValue (string).public (bool assetValueWasChanged, string assetValue) Execute(string assetName, string assetValue)public (bool assetValueWasChanged, string assetValue) Execute(string assetName, string assetValue) - Use the
GetAssetcoded automation API to retrieve the current value of the specified asset using theassetNameparameter. - Store the previous asset value in the
previousAssetValuevariable .var previousAssetValue = system.GetAsset(assetName).ToString();var previousAssetValue = system.GetAsset(assetName).ToString(); - Compare the previous asset value with the input asset value using the
Equalsmethod. - If the values are equal, return
(false, assetValue)to indicate that the asset value was not changed. - If the values are different, use the
SetAssetcoded automation API to update the asset value to the inputassetValue. - Return
(true, previousAssetValue)to indicate that the asset value was changed, along with the previous asset value.
if (previousAssetValue.Equals(assetValue)) { return (assetValueWasChanged: false, assetValue: assetValue); } else { system.SetAsset(assetValue, assetName); return (assetValueWasChanged: true, assetValue: previousAssetValue); }if (previousAssetValue.Equals(assetValue)) { return (assetValueWasChanged: false, assetValue: assetValue); } else { system.SetAsset(assetValue, assetName); return (assetValueWasChanged: true, assetValue: previousAssetValue); } - Give the following return arguments to the
-
Create a low-code workflow. For this example, name it
WorkflowUsingCodedAutomation. -
Add an Assign activity and assign a value to the
assetValuevariable. -
Add an Invoke Workflow File activity and invoke the
CodedResetAssetValue.cscoded automation. Add the required arguments.Note:For Windows projects: In the Invoke Workflow File activity, select Browse for File and change the file extensions you're browsing for, from Workflow Files (
*.xaml,*.uiwf) to All Files (*.*). This allows you to view all files, including.cs.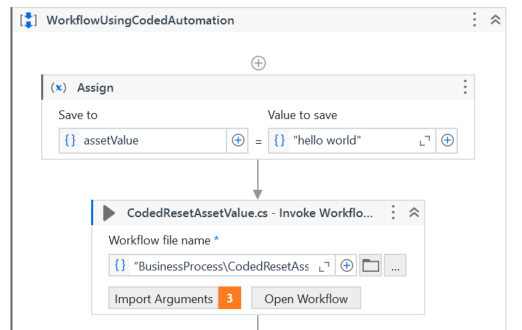
-
Add an If activity, and log messages for the scenarios where an asset value remains unchanged, and for the scenario where an asset value is updated.